引言
使用终端ssh登录Linux操作系统的控制台后,会出现一个提示符号(例如:#或~),在这个提示符号之后可以输入命令,Linux根据输入的命令会做回应,这一连串的动作是由一个所谓的Shell来做处理。Shell是一个程序,最常用的就是Bash,这也是登录系统默认会使用的Shell。
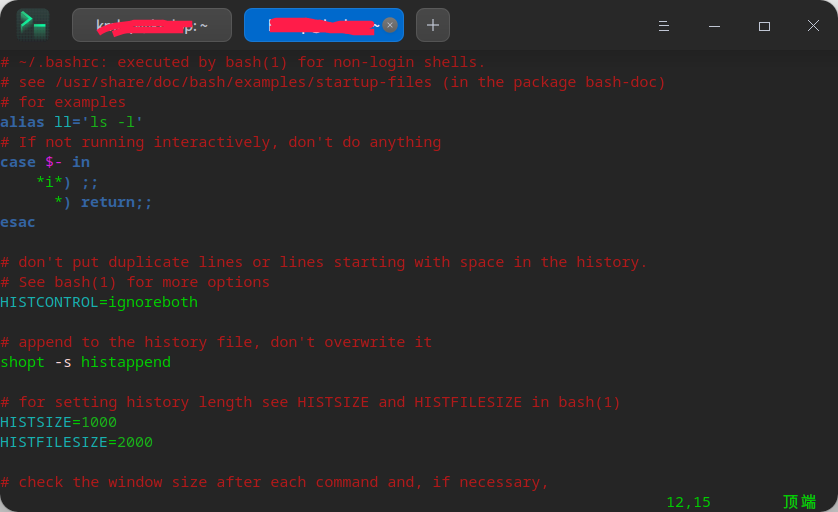
对于个别用户的启动配置文件
hello@hello:~$ head ~/.bashrc
# ~/.bashrc: executed by bash(1) for non-login shells. 对于非登录shell,由bash(1)执行hello@hello:~$ head ~/.profile
# ~/.profile: executed by the command interpreter for login shells. 由命令解释器为登录shell执行对于全部用户的启动配置文件
hello@hello:~$ head /etc/bash.bashrc
# System-wide .bashrc file for interactive bash(1) shells. 用于交互式bash(1) shell的系统级的.bashrc文件。
hello@hello:~$ head -1 /etc/profile
# /etc/profile: system-wide .profile file for the Bourne shell (sh(1)) Bourne shell的系统级.profile文件四个文件 .bashrc .profile 和/etc/bash.bashrc /etc/profile
bashrc和profile的差异
从上面的英文描述可以知道,bashrc和profile(配置文件)的差异在于:
1. bashrc是在系统启动后就会自动运行。
2. profile是在用户登录后才会运行。
3. 进行设置后,可运用source bashrc命令更新bashrc,也可运用source profile命令更新profile。
PS:通常我们修改bashrc,有些linux的发行版本不一定有profile这个文件,本文用的系统是Uos 20
4. /etc/profile中设定的变量(全局)的可以作用于任何用户,而~/.bashrc等中设定的变量(局部)只能继承/etc/profile中的变量,他们是”父子”关系。
补充介绍
另外,需要补充说明介绍bashrc相关的几个文件:
~/.bash_profile: 每个用户都可使用该文件输入专用于自己使用的shell信息,当用户登录时,该文件仅仅执行一次!默认情况下,他设置一些环境变量,执行用户的.bashrc文件。
~/.bash_logout: 当每次退出系统(退出bash shell)时,执行该文件。
~/.bash_profile 是交互式、login方式进入bash运行的,~/.bashrc是交互式non-login方式进入bash运行的,通常二者设置大致相同,所以通常前者会调用后者。
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END